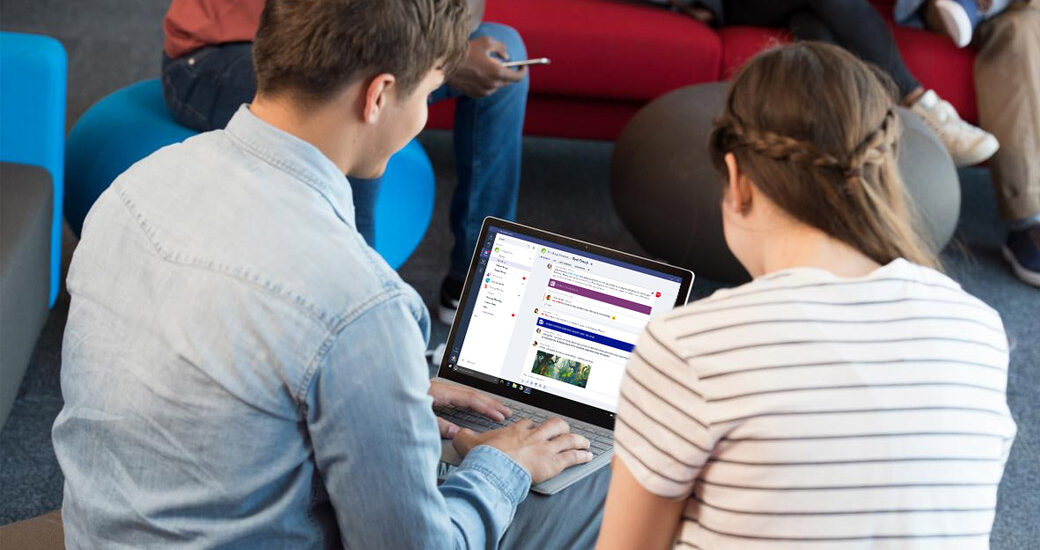



Welcome to the exciting world of blended learning! In today’s ever-evolving educational landscape, traditional classroom instruction is no longer the only option. Blended learning has emerged as a powerful approach that combines online and offline teaching methods to create a dynamic and personalized learning experience.
So, what exactly is blended learning? Well, imagine a classroom where students can seamlessly switch between digital platforms and face-to-face interactions. It’s like having the best of both worlds – harnessing the power of technology while still enjoying the benefits of in-person collaboration.
In this costume college article, we will delve into the four key models of blended learning. Each model offers its own unique advantages and disadvantages, catering to different preferences and goals. Whether you’re an educator looking to enhance your teaching strategies or a student seeking more flexibility in your studies, there’s bound to be a model that suits your needs.
Are you ready to explore these innovative approaches? Let’s dive right in!
Blended learning is a revolutionary educational approach that combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning. It’s all about finding the perfect balance between digital tools and in-person interactions to create a dynamic and engaging learning environment.
In this model, students have the opportunity to access course materials, resources, and assignments through online platforms. This allows for flexibility in terms of when and where they can study. Whether it’s watching instructional videos, participating in online discussions, or completing interactive quizzes, technology plays a crucial role in supporting student learning.
However, blended learning also emphasizes the importance of face-to-face interactions. Classroom time is utilized for collaborative activities, group projects, and direct instruction from teachers. By combining digital tools with traditional teaching methods, educators can personalize the learning experience based on individual student needs and provide immediate feedback.
One of the key benefits of blended learning is its ability to cater to different learning styles and paces. Students who thrive in independent study settings can complete online modules at their own pace while those who prefer social interaction can engage with peers during classroom sessions.
Furthermore, blended learning promotes self-directedness as students take ownership of their education by managing their time effectively and developing essential skills such as critical thinking and problem-solving.
Blended learning, a combination of traditional face-to-face instruction and online learning, has gained popularity in recent years for its ability to enhance student engagement and personalize the learning experience. There are four key models of blended learning that educators can implement in their classrooms: the Rotation model, the Flex model, the A La Carte model, and the Enriched Virtual model.
The Rotation model involves students rotating between different stations or modalities throughout a class period. This allows them to receive direct instruction from the teacher as well as engage in independent or collaborative online activities. The Flex model gives students more control over their learning by allowing them to customize their schedule and pace with support from teachers when needed.
In contrast, the A La Carte model provides students with online courses that supplement their traditional brick-and-mortar classes. This allows for greater flexibility in course selection and scheduling. The Enriched Virtual model combines face-to-face classroom instruction with online coursework outside of school hours.
Each of these models offers unique advantages and disadvantages depending on factors such as student needs, available resources, and instructional goals. Educators must consider these factors when determining which blended learning approach is most suitable for their specific teaching context.
By exploring these four key models of blended learning, educators can make informed decisions about how best to integrate technology into their classrooms while promoting student success and engagement. Whether it’s through rotation-based activities or personalized schedules facilitated by flexible online platforms – there’s a blend out there for every educator!
1. Rotation model: One of the key advantages of the rotation model is its flexibility. Students have the opportunity to work at their own pace and receive individualized instruction, which can lead to better understanding and retention of material. Additionally, this model allows for a mix of online and offline activities, catering to different learning styles.
However, one disadvantage is that it requires careful planning on the part of teachers to ensure smooth transitions between stations or activities. It also relies heavily on technology infrastructure, so schools with limited resources may face challenges in implementing this model effectively.
2. Flex model: The flex model offers great autonomy for students as they have control over their learning path and can set their own pace. This encourages self-motivation and independence, essential skills for lifelong learning.
On the downside, this model requires strong time management skills from students as they need to balance their responsibilities across various subjects or modules independently. You can view website to understand and learn some key management skills. Additionally, some students may struggle with self-discipline without direct supervision from a teacher.
3. A la carte model: This personalized approach allows students to choose specific courses or modules according to their interests or academic needs. It provides flexibility in scheduling classes while still receiving guidance from qualified instructors.
Nevertheless, one drawback is that it may limit opportunities for social interaction among peers since students are not attending all classes together like in traditional settings. Furthermore, schools must carefully consider course availability and quality when offering an extensive range of options through an a la carte system.
4. Enriched virtual model: The enriched virtual model combines both face-to-face instruction with online components seamlessly integrated into coursework structure. This allows for greater engagement and collaboration among students while providing access to additional resources beyond what’s available in traditional classrooms alone.
However beneficial this hybrid approach might be there will always be challenges associated with maintaining consistent communication channels between teachers and remote learners due mainly because technology issues could arise unexpectedly disrupting synchronous interactions when they are needed.
Each blended learning model has its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
When it comes to blended learning, choosing the right model can make all the difference in achieving your educational goals. With four key models to choose from, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, it’s important to consider what will work best for you.
The first model is the Rotation model. This approach involves students rotating between different learning stations, such as online activities, small group discussions, and individual assignments. It allows for flexibility and personalized instruction but may require a lot of planning and organization.
Next up is the Flex model. In this model, students primarily learn online at their own pace and have access to support from teachers as needed. It offers a self-paced learning experience but requires students to be motivated and independent learners.
The third option is the Self-blend model where students combine traditional classroom instruction with online learning outside of school hours. This provides a balance between face-to-face interaction with teachers and the flexibility of online resources.
We have the Enriched-virtual model which blends traditional classroom instruction with virtual components on a regular basis. Students attend classes part-time while also engaging in online coursework during non-classroom hours.
So how do you determine which one suits you best? Consider factors like your personal learning style, available resources, and level of technological comfort. Reflecting on these aspects will help guide your decision-making process when selecting an appropriate blended learning model that aligns with your needs and preferences.
Remember that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution – what works for someone else may not work for you! Take time to research each model thoroughly before making an informed choice about which one will ultimately benefit your educational journey
In today’s ever-evolving educational landscape, blended learning has emerged as a powerful approach to instruction that combines the best of traditional classroom settings with the flexibility and interactivity of online learning. By integrating face-to-face and digital components, educators have the opportunity to create dynamic and personalized learning experiences for their students.
Throughout this article, we explored four key models of blended learning: Rotation Model, Flex Model, A La Carte Model, and Enriched Virtual Model. Each model offers unique advantages and disadvantages depending on factors such as student needs, resources available, and instructional goals.
The Rotation Model allows for targeted instruction while maintaining some level of class cohesion. The Flex Model provides individualized pacing and self-directed learning opportunities. The A La Carte Model offers flexibility in course selection but may result in less peer interaction. The Enriched Virtual Model blends face-to-face teaching with online elements to enhance student engagement.
When deciding which model is right for you or your institution, it is crucial to consider various factors such as access to technology, teacher comfort level with online platforms, student support services available, curriculum requirements, and desired outcomes. It may also be beneficial to pilot different models or seek input from other educators who have implemented blended learning approaches.
Remember that successful implementation requires careful planning and ongoing evaluation to ensure that both teachers’ instructional needs are met while providing students with meaningful learning experiences.
Blended Learning continues to evolve as technology advances; therefore staying informed about new pedagogical strategies can help educators stay ahead of the curve in providing quality education tailored to today’s learners.